
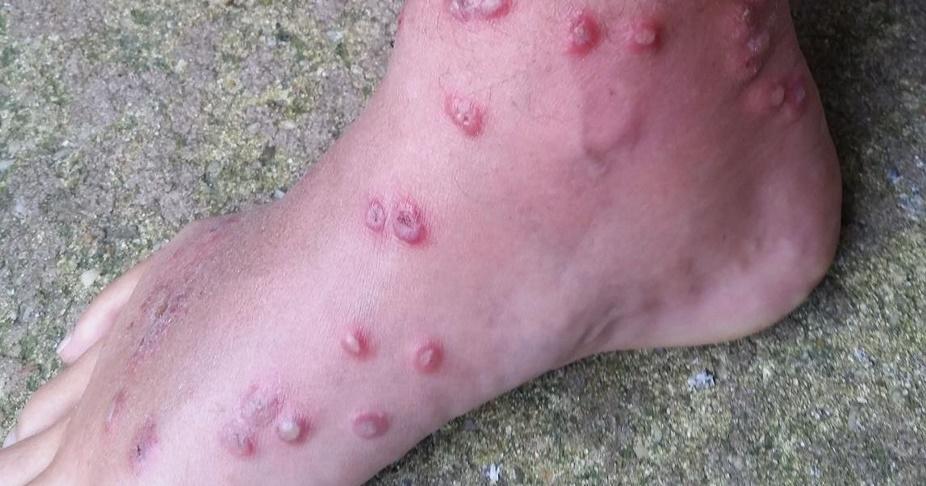
Swimmer’s itch usually resolves within 1–3 weeks without treatment. Short course of oral corticosteroid for a severe reaction.
#SWIMMERS ITCH TODDLER SKIN#
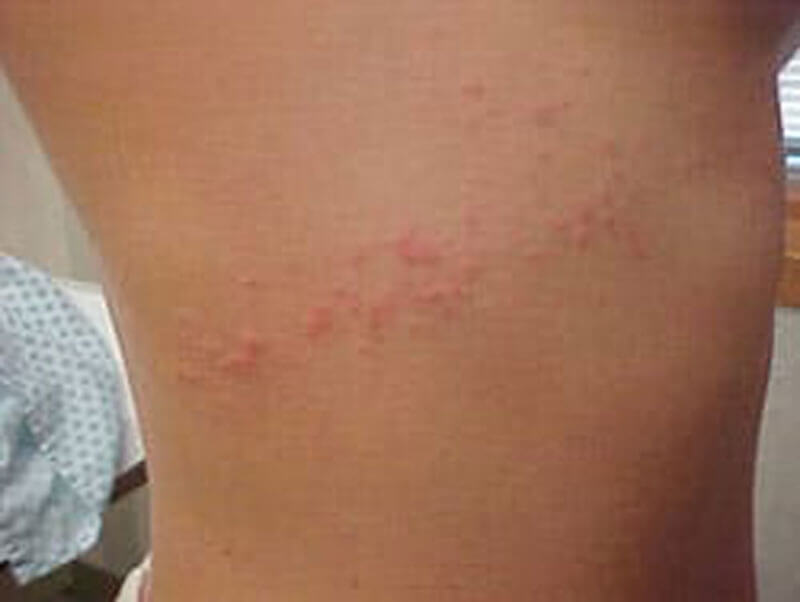

The itching occurs within 48 hours and may last up to 7 days. After the initial transient itching it will disappear without treatment. Use of chemical molluscicides such as copper sulphate or copper carbonate in small lakes to kill potentially infested snails. Swimmer's itch is a patchy red pinpoint skin rash associated with itching on the parts of the body that have been in the water.Reduce vegetation in high-risk areas to make the environment less favourable for the water snails.Feed birds with a drug to treat the parasite.To reduce parasite numbers in the environment: What is the treatment for swimmer’s itch? Preventative measures While the parasite’s preferred host is the specific bird. These parasites are released from infected snails into fresh and salt water (such as lakes, ponds, and oceans). What is the differential diagnosis for swimmer’s itch? Swimmer’s itch, also called cercarial dermatitis, appears as a skin rash caused by an allergic reaction to certain microscopic parasites that infect some birds and mammals. Cercariae may accidentally attach to human skin, penetrate the skin, die, and cause a local allergic reaction. Cercariae may penetrate the skin or are ingested by the aquatic bird/animal, develop into an adult worm, and the cycle starts again. The condition is a rash brought on by the bodys allergic reaction to the larvae of. The miracidium enters the snail, elongates into a sporocyst, then matures into a cercaria which burrows out of the snail into the water. Its most common in freshwater lakes and ponds, but can occur in saltwater. An egg hatches in the water to become a free-swimming miracidium in search of a specific snail species. The adult worm lives in a bird/animal, and the eggs are excreted via the intestines in the faeces. Schistosomes are parasitic flatworms with a lifecycle that involves aquatic birds (eg, ducks, geese, gulls, swans) or mammals (eg, beavers, muskrats), specific species of aquatic snails, and warm fresh or salt water. Swimmer’s itch is a disease of aquatic birds and humans are accidentally affected. However, it is only after repeated exposure to cercariae that the allergy develops and a rash eventuates. Young children are particularly susceptible as they tend to remain in shallow warm water where the snails are found in the highest numbers. Swimmer’s itch can affect anyone swimming in waters with infested snails.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
